Gum Disease Treatment
Introduction:
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common dental condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It ranges from mild inflammation of the gums to severe damage to the soft tissue and bone that support the teeth. Fortunately, with proper diagnosis and treatment, gum disease can be managed effectively, preserving both oral health and overall well-being.
Signs and Symptoms:
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of gum disease is crucial for early detection and intervention. These may include:
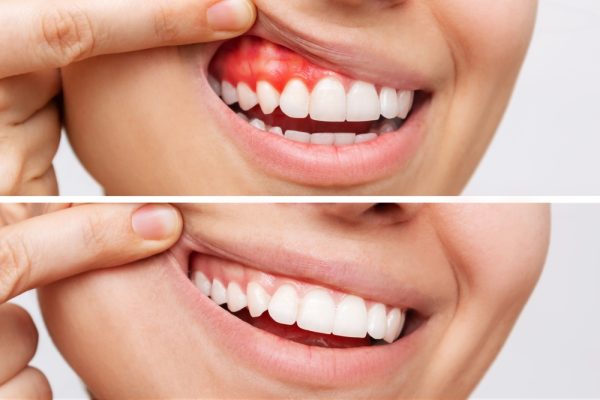
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing
- Receding gums, causing teeth to appear longer
- Persistent bad breath
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Changes in the fit of dentures
Causes of Gum Disease:
Gum disease typically develops due to poor oral hygiene habits that allow plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, to accumulate along the gumline. Factors that increase the risk of gum disease include smoking, hormonal changes, certain medications, diabetes, and genetic predisposition.
Types of Gum Disease:
- Gingivitis: This is the earliest stage of gum disease, characterized by inflammation of the gums. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to more severe forms of periodontal disease.
- Periodontitis: In this stage, the inflammation extends below the gumline, causing damage to the supporting bone and tissues. Without intervention, periodontitis can lead to tooth loss.
Gum Disease Treatment:
Effective treatment for gum disease aims to reduce inflammation, eliminate infection, and restore gum and bone health. Treatment options may include:
- Professional Dental Cleaning: Removing plaque and tartar buildup through professional cleaning is essential for controlling gum disease.
- Scaling and Root Planing: This deep cleaning procedure involves removing plaque and tartar from below the gumline and smoothing the tooth roots to prevent bacterial reattachment.
- Antibiotic Therapy: Antibiotics, in the form of mouth rinses, gels, or oral medications, may be prescribed to control bacterial infection and promote healing.
- Surgical Intervention: In advanced cases of gum disease, surgical procedures such as flap surgery, bone grafting, or tissue regeneration may be necessary to repair damaged tissues and restore oral health.
Prevention:
Preventing gum disease starts with practicing good oral hygiene habits, including:
- Brushing teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Flossing daily to remove plaque from between teeth and along the gumline.
- Visiting the dentist regularly for professional cleanings and oral exams.
- Avoiding tobacco use and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Contact Us
Quality Dental Group
Our team of experienced general dentist and specialists is dedicated to delivering timely and effective dental care, offering personalized solutions for people of all ages and needs.
